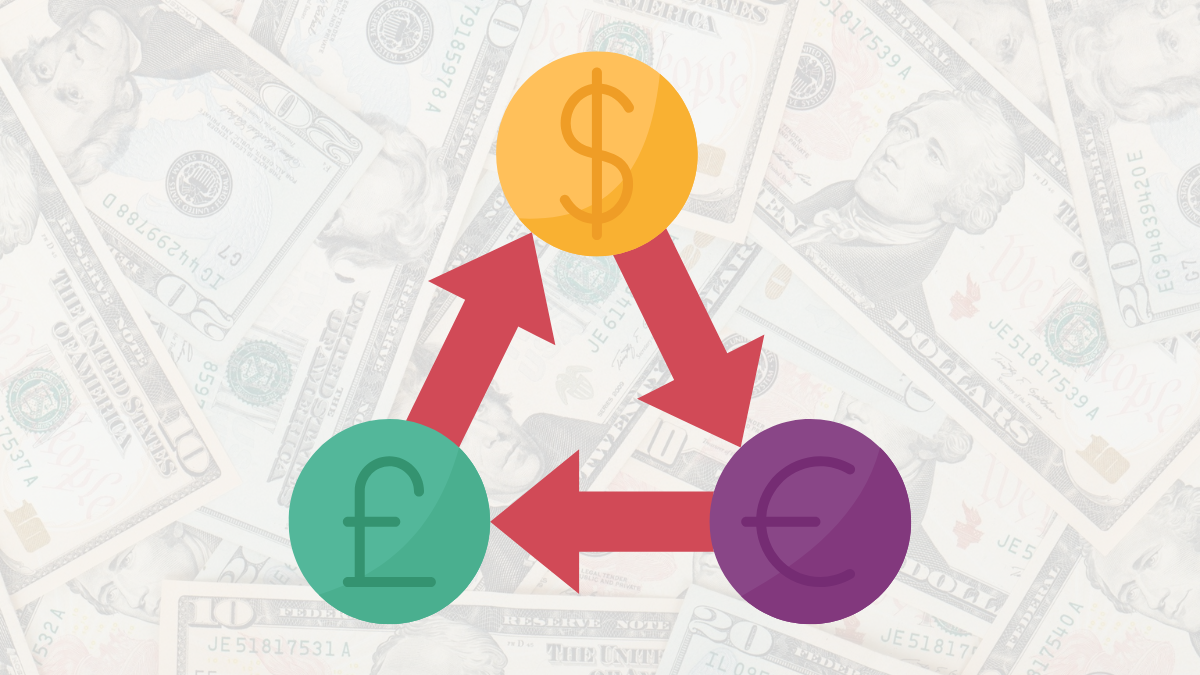
What is Arbitrage Trading?
Arbitrage trading refers to a strategy where traders buy and sell simultaneously in different markets, taking advantage of price differences.For example: Suppose in the Tokyo market, the exchange rate for EUR / USD is 1.1000, while in the New York market it is 1.1002. The trader can buy euros in Tokyo while selling euros in New York, earning a price difference of 0.0002.
In foreign exchange margin trading, arbitrage can occur in:
- Exchange rate differences between different exchanges.
- Price differences within the same exchange due to time delays or pricing errors.
- Mispricing between multiple currency pairs (e.g., triangular arbitrage).
Types of Arbitrage in Foreign Exchange Margin Trading
Foreign exchange margin trading provides diverse opportunities for arbitrage, here are common types of arbitrage:1. Spatial Arbitrage: Price differences between different exchanges. For example, there may be slight differences in market exchange rates between London and Sydney, providing arbitrage opportunities.
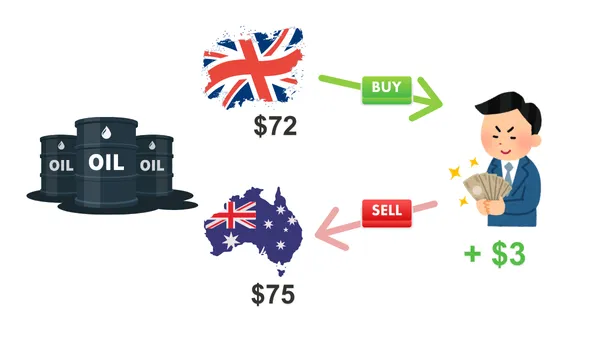
2. Temporal Arbitrage: Some trading platforms may have delays in quoting, leading to temporary price distortions. Traders can seize these delays to achieve arbitrage.

3. Triangular Arbitrage: Finding mispricing in exchange rates through three currency pairs. For example, utilizing the relationship between USD, EUR, and JPY for quick cross-currency trading.
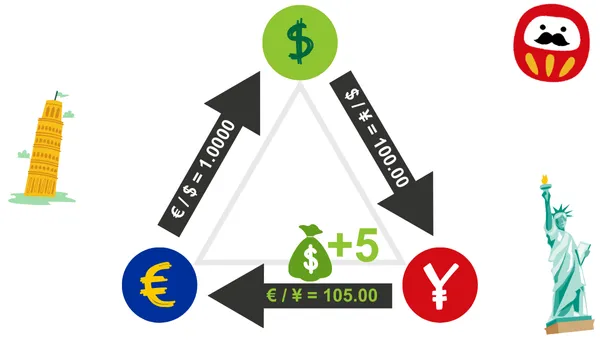
Why is Foreign Exchange Margin Suitable for Arbitrage Trading?
Foreign exchange margin trading is an ideal area for arbitrage due to its market characteristics:- Global Market Operating 24/7: The foreign exchange market is one of the few markets in the world that operates 24 hours a day, meaning arbitrage opportunities can arise at any time.
- Leverage Effect: Foreign exchange margin allows traders to control larger trading amounts with smaller capital, amplifying potential arbitrage profits.
- Diverse Currency Pairs: The foreign exchange market offers hundreds of currency pairs, especially with high liquidity among major currency pairs, providing greater arbitrage space.
Challenges and Risk Management in Arbitrage Trading
Although arbitrage trading seems low-risk, it still faces the following challenges:- Transaction Costs: Fees and spreads can erode arbitrage profits, so it is necessary to choose low-cost trading platforms.
- Increased Market Efficiency: With the prevalence of algorithmic trading, market inconsistencies are quickly corrected, making arbitrage opportunities rare and short-lived.
- Slippage and Execution Risk: High-frequency volatility can lead to slippage, where the trading price deviates from expectations, thus reducing or even erasing profits.
Practical Tools and Strategies for Arbitrage Trading
Successful arbitrage trading relies on the following tools and strategies:- Automated Trading Software: Utilizing automated programs to detect market price differences and execute quick trades. For example, MetaTrader or professional algorithmic trading systems.
- Fast Internet Connection: Delays are the enemy of arbitrage trading. An efficient internet connection helps reduce delays and ensures the accuracy of trade execution.
- Risk Management Tools: Setting stop-loss and profit target levels to reduce risks from market volatility.
Conclusion
Arbitrage trading is an efficient strategy in the foreign exchange margin market, highly attractive for traders looking to reduce risk and achieve stable returns. However, successful arbitrage requires quick action, support from automated tools, and a clear understanding of market efficiency and risks. It is hoped that through this article, you can gain a deeper understanding of arbitrage trading and master its core essence in practical operations.
Hi, we are the Mr.Forex Research Team
Trading requires not just the right mindset, but also useful tools and insights. We focus on global broker reviews, trading system setups (MT4 / MT5, EA, VPS), and practical forex basics. We personally teach you to master the "operating manual" of financial markets, building a professional trading environment from scratch.
If you want to move from theory to practice:
1. Help share this article to let more traders see the truth.
2. Read more articles related to Forex Education.
Trading requires not just the right mindset, but also useful tools and insights. We focus on global broker reviews, trading system setups (MT4 / MT5, EA, VPS), and practical forex basics. We personally teach you to master the "operating manual" of financial markets, building a professional trading environment from scratch.
If you want to move from theory to practice:
1. Help share this article to let more traders see the truth.
2. Read more articles related to Forex Education.