Foreign Exchange Margin Terminology Quick Reference
1. Margin:
Margin is the funds that traders need to deposit when opening or maintaining a trade, serving as a guarantee for the transaction. It is a "deposit," not the total funds for trading, just a part, and is closely related to leverage.2. Leverage:
Leverage refers to the ability of traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. It is expressed in ratio form, for example, 100: 1, meaning that with 1 dollar, you can control a trading position of 100 dollars.3. Used Margin:
Used Margin is the total amount of margin required to maintain all open trades. This portion of funds has been "locked" in the trades and cannot be used to open new positions.4. Free Margin:
Free Margin is the remaining funds after opening or maintaining existing positions, which can be used to open new trades.Formula: Free Margin = Equity - Used Margin.
5. Equity:
Equity is the total funds in the account, including the account balance and the floating profit and loss of open trades.Formula: Equity = Account Balance + Floating P/L.
6. Account Balance:
Account Balance is the available cash in your account, including the profit and loss of all closed trades, but excluding floating profit and loss. Only after the trade is closed will the floating profit and loss be accounted for in the account balance.7. Floating P/L and Unrealized P/L:
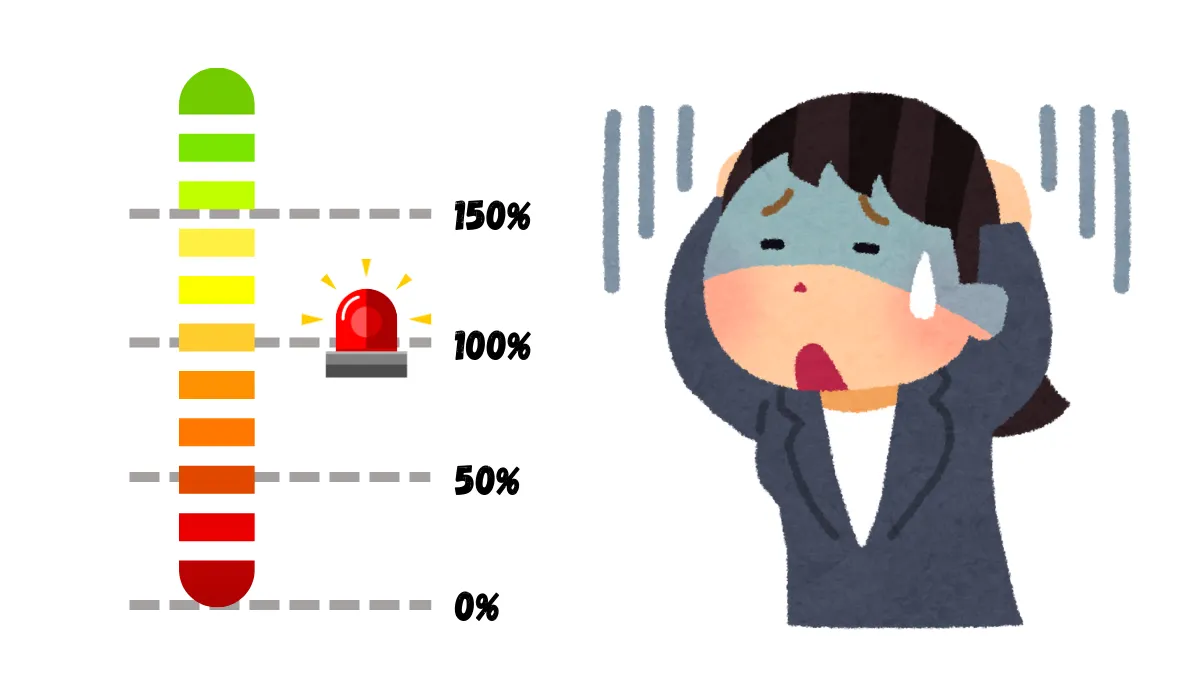
Floating P/L refers to the current profit and loss of open trades. When market prices fluctuate, floating P/L also varies, and it only becomes realized profit and loss when the position is closed.8. Margin Level:
Margin Level is the ratio of equity to used margin, usually expressed as a percentage.Formula: Margin Level = (Equity / Used Margin) x 100.
If the margin level falls to a certain critical point, it may trigger a margin call or forced liquidation.
9. Margin Call:
When the margin level drops to a percentage set by the broker (for example, 100%), the broker will issue a margin call notification, requiring you to add funds or close part of your positions to maintain existing trades.10. Stop Out or Liquidation:
Stop Out refers to when the margin level falls to a lower percentage (for example, 50%), the broker will automatically close part or all positions to prevent further losses in the account.11. Margin Requirement:
Margin Requirement is the minimum funds required by the broker to open a certain trading position, usually expressed as a percentage.For example, a margin requirement of 1% means you need to provide 1% of the total trade value as margin.
12. Stop Out Level:
Stop Out Level refers to the percentage level at which the broker will start to automatically close positions when the margin level falls to the minimum limit set by the broker (for example, 50%).13. Leverage Ratio:
Leverage Ratio is the ratio between margin and tradable capital. The higher the leverage ratio, the less margin traders can use to control larger positions, but the risk also increases accordingly.
Hi, we are the Mr.Forex Research Team
Trading requires not just the right mindset, but also useful tools and insights. We focus on global broker reviews, trading system setups (MT4 / MT5, EA, VPS), and practical forex basics. We personally teach you to master the "operating manual" of financial markets, building a professional trading environment from scratch.
If you want to move from theory to practice:
1. Help share this article to let more traders see the truth.
2. Read more articles related to Forex Education.
Trading requires not just the right mindset, but also useful tools and insights. We focus on global broker reviews, trading system setups (MT4 / MT5, EA, VPS), and practical forex basics. We personally teach you to master the "operating manual" of financial markets, building a professional trading environment from scratch.
If you want to move from theory to practice:
1. Help share this article to let more traders see the truth.
2. Read more articles related to Forex Education.