Basic Concept of Spatial Arbitrage
Spatial arbitrage is a strategy that involves trading based on exchange rate differences between different markets or platforms.
Case Analogy: Assuming the instrument you operate is cheaper in Tokyo and more expensive in New York, you can buy the instrument in Tokyo and sell it in New York to profit from the price difference. In the foreign exchange market, such arbitrage does not require the physical transportation of the instrument, only the rapid execution of exchange rate trades.
In the foreign exchange market, this price difference is usually caused by factors such as market quote delays, differences in trading volume, or insufficient liquidity. By detecting and executing trades in real-time, traders can achieve stable returns.
Practical Steps for Spatial Arbitrage
Spatial arbitrage requires accurate planning and execution. Here are the main steps for practical operation:- Select Target Currency Pair: Choose highly liquid Major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, as they are more likely to exhibit market differences.
- Look for Market Price Differences: Use multi-platform tools (like MetaTrader) to compare exchange rate quotes from different markets and quickly identify arbitrage opportunities.
- Execute Synchronous Trades: Buy currency in the market with the lower price while simultaneously selling in the market with the higher price. Ensure execution speed is fast enough to avoid the disappearance of the price difference.
- Calculate Profits and Costs: Before executing trades, calculate the spread, transaction fees, and slippage costs to confirm that potential profits are sufficient to cover these costs.
Example: Application of Spatial Arbitrage in the Foreign Exchange Margin Market
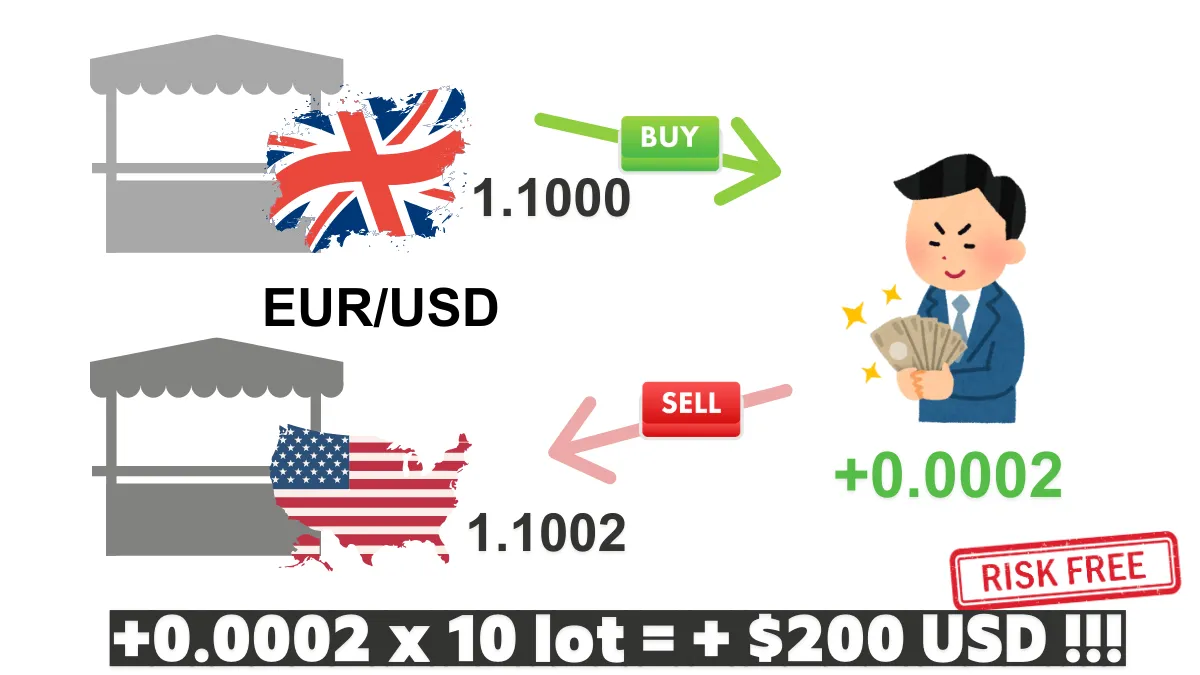
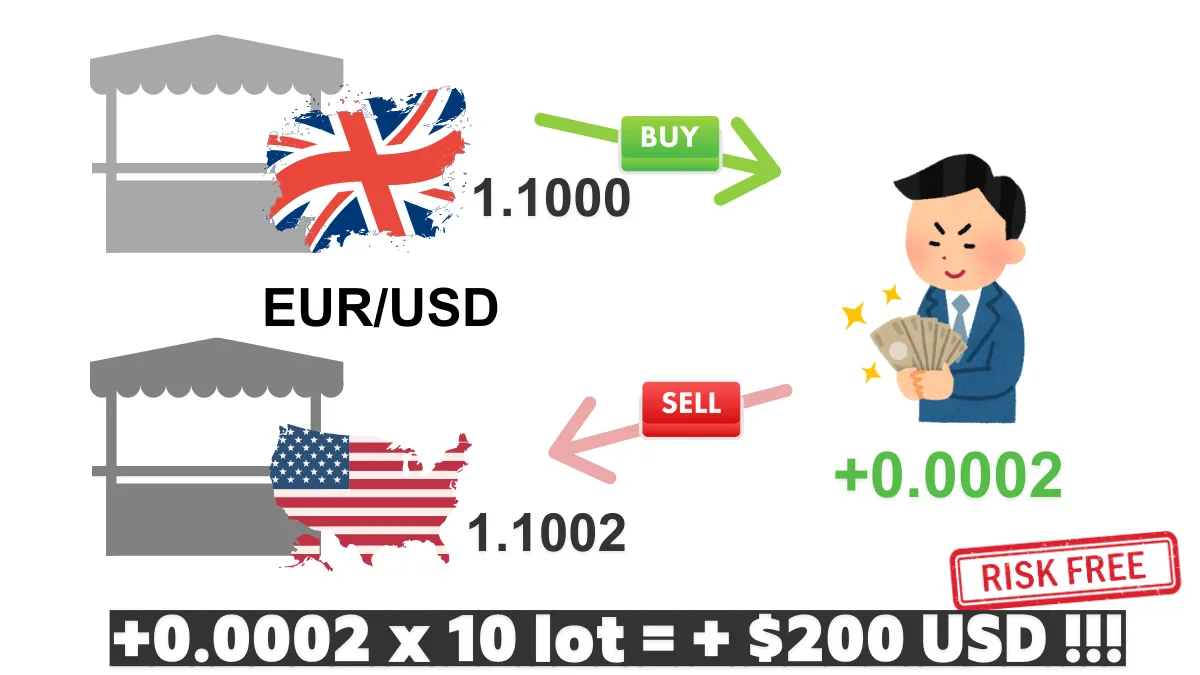
Case 1: Exchange Rate Difference Between London and New York MarketsAssume the quote for EUR/USD in the London market is 1.1000, while the quote in the New York market is 1.1002.
You can buy EUR in the London market at 1.1000 and sell it in the New York market at 1.1002, achieving a profit of 0.0002 per unit. Assuming 1 lot represents a trading volume of 100,000 units, if you trade 10 lots, the total trading volume is 100,000 units × 10 times, which equals 1,000,000 units. Therefore, the profit calculation is as follows: 0.0002 × 1,000,000 = 200 USD. This indicates that through this arbitrage operation, you can achieve a stable profit of 200 USD in a short time, provided that trading costs such as fees and slippage are low and do not significantly erode this profit.
Case 2: Opening Arbitrage Between Asian and European Markets
The Asian market has lower trading volume during early trading hours, leading to relatively larger exchange rate fluctuations. After the European market opens, exchange rates are usually more stable. Traders can take advantage of the price differences during this period for arbitrage operations.
These cases demonstrate the potential profits of spatial arbitrage, but also remind traders that they must complete trades in a very short time.
Risks and Challenges of Spatial Arbitrage
- Impact of Trading Costs: Transaction fees, spreads, and slippage may erode arbitrage profits, making it crucial to choose low-cost trading platforms.
- Increased Market Efficiency: As market automation increases, price difference opportunities often disappear quickly, requiring traders to have fast execution capabilities.
- Technical Dependence: Spatial arbitrage relies on efficient algorithmic trading and stable internet connections; technical errors may lead to trade failures.
- Leverage Risk: While leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses, so traders should use leverage tools cautiously.
Practical Tools and Strategies
To better achieve spatial arbitrage, traders can adopt the following tools and strategies:
- Multi-Platform Comparison Tools: Use multi-platform price monitoring tools (such as cTrader or professional algorithmic trading systems) to quickly identify market differences.
- Automated Trading Software: Utilize algorithmic trading programs to automatically execute arbitrage operations, reducing the risk of delays in manual operations.
- Risk Management Strategies: Set stop-loss and take-profit points to ensure timely exit from trades when market conditions are unfavorable.
Conclusion: Seizing Arbitrage Opportunities in Foreign Exchange Margin
Spatial arbitrage is a low-risk, high-efficiency trading strategy, and its application in the foreign exchange margin market can help traders achieve stable returns. However, to successfully implement spatial arbitrage, one needs to have efficient execution capabilities, accurate market analysis, and comprehensive risk control strategies.
Through this article, you can not only gain an in-depth understanding of the core techniques of spatial arbitrage but also use case studies and tool recommendations to enhance trading effectiveness. I hope this article can serve as an important resource for your foreign exchange trading strategy, helping you progress steadily in the market!
Hi, we are the Mr.Forex Research Team
Trading requires not just the right mindset, but also useful tools and insights. We focus on global broker reviews, trading system setups (MT4 / MT5, EA, VPS), and practical forex basics. We personally teach you to master the "operating manual" of financial markets, building a professional trading environment from scratch.
If you want to move from theory to practice:
1. Help share this article to let more traders see the truth.
2. Read more articles related to Forex Education.
Trading requires not just the right mindset, but also useful tools and insights. We focus on global broker reviews, trading system setups (MT4 / MT5, EA, VPS), and practical forex basics. We personally teach you to master the "operating manual" of financial markets, building a professional trading environment from scratch.
If you want to move from theory to practice:
1. Help share this article to let more traders see the truth.
2. Read more articles related to Forex Education.